EoC system in an old castle
AXING shows IP distributions fpr cable networks
4 November 2016 | England is famous for its old castles and stately homes. These days, they usually accommodate luxury hotels, golf clubs or luxury spa hotels.

Champneys operates four luxury spa hotels in England. To meet today’s technical requirements, it is currently executing extensive modernization measures, which also include the replacement of TV sets in the hotel rooms. In addition to DVB-T signals, the new TV system requires a network port so that the TV sets can be controlled from a central point.
IP distribution plays a crucial role in any modern communications system. However, the rooms do not have any network or LAN connection. This meant that a decision had to be made on how to ensure that the signals were able to reach the users. This is the same question that invariably arises with buildings such as hospitals, hotels, airports and the like during ongoing operations. The installation of new infrastructure leads to operational restrictions and thus to losses of revenue or causes immense renovation costs. For this reason, Champney opted for a solution with EoC “Ethernet over Coax” developed by AXING.
This technology involves the use of the existing coaxial infrastructure to automatically create a virtual LAN network. To achieve this, only a passive return path must be available in the eoaxial cable network as the EoC signals must be transmitted bidirectionally in the 5 .. . 65 MHz frequency range. lt may also be necessary to replace the amplifiers. All the other passive components only need to be able to transmit the return frequency range.
Obviously, other technical solutions would also have been possible but they are not optimized for this particular application. Cable network operators use in their networks DOCSIS technology, which is a stable and reliable IP transmission method. However, the cost of the CMTS is not inconsiderable. Accordingly, the cost per port is quite high in the case of small buildings. With DOCSIS technology, a CMTS is installed at the source and the users receive a cable modern. Currently, the maximum data rate in real operations stands at around 400 Mbps. At the same time, all the users share the bandwidth, while the cable network must be modernized to ensure that it can accommodate return paths. In most cases, this means that the amplifiers must be replaced. Very occasionally, however, it may also be possible to add a return path amplifier.
EoC technology
Based on the international IEEE 1901 standard, EoC uses the lower frequency range of 2 … 68 MHz of the cable network, where there is very low attenuation in the coaxial cable. This means that distances of up to 700 m can be bridged. Thanks to OFDM (orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing) modulation, which is also used in DVB-T transmission, it is highly resilient to interference.
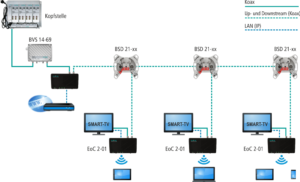
EoC technology by AXING offers different modes of operation. The “peer to peer” operating mode is intended for home applications, in which case the modems communicate with each other, meaning that the data is sent to all modems from any point. The “masterslave” operation mode is for professional applications. Communications are rendered from a master to the slaves and from the slave to the master. As no communication is possible between them, this helps to control traffic. Figure 2 shows the typical structure of a master slave system.
There are various EoC applications, such as private IP distribution, where terminals are linked to the Internet and only an antenna outlet is located close to the terminal device. The structure of the antenna distribution system does not matter as either SAT IF distribution or broadband distribution technologies can be used. The topology of the distribution network is also irrelevant – either a tree net structure or star wiring can be used. The IP signals are fed into the distribution network via the modern at the antenna socket at the transfer point or behind the headend. Up to 64 modems can be connected within a network, with intelligent clustering permitting multiple networks to be established.
The data throughput reaches a maximum of 500 Mbps (gross), which is equivalent to about 230 Mbps (net). Thus, multiple HD streams can be transmitted simultaneously. OoS can be used to assign individual services a higher priority, while 128-bit AES encryption prevents intrusion on the part of unauthorized users.
All-IP network
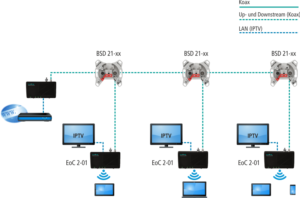
The EoC devices from AXING can also be used just as effectively in professional applications, meaning that they can be utilized in all-IP networks. In the typical IP structure the switch is located at the source or at the master. From there, the IP signals are sent to the slave devices across the coaxial network to which the terminals are connected. In order to create an all-IP network via the coaxial cables, the HF signals are first deactivated, resulting in a solely passive coaxial network. This means that no active components (amplifiers) are necessary. The IP signal is now connected via a switch to one or more EoC master modems at the central place where the amplifier used to be. Smaller sub-networks are created by means of clustering, thus ensuring that the necessary data rate can be transferred. Figure 3 shows the conversion of a broadband cable network into an all-IP network.
Summary
These days, old coaxial cable systems can be used for advanced communications. With the help of the EoC technolO’t:f, it is possible to give coaxial cable a new lease on life. Thanks to the variety of possible applications, all types of distribution networks can be used for this technolo’t:f, regardless of whether they are SAT IF systems, CATV systems with a tree network or a star structure. The system is suitable for use in private homes as well as for professional applications in hotels, hospitals, airports, etc.Intelligent clustering can be used to create subnets and to split the total number of terminals. As there are two network connections per unit a further IP application is possible. Even with a “bad” connection, “good” transmission performance is still possible thanks to OFDM. Another version includes an integrated WiFi module in addition to the two network connections.